EV Chargers
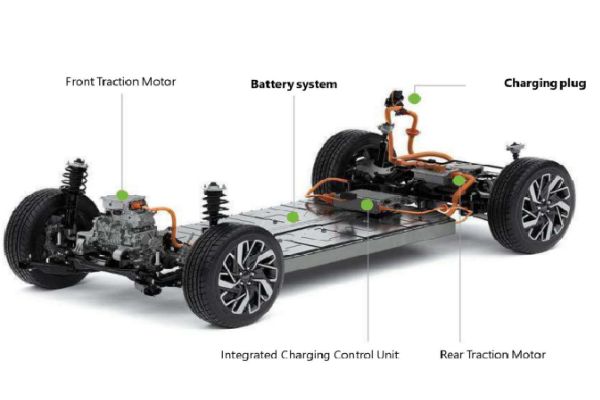
Evs have approx. 90% fewer moving parts than an ICE(internal combustion engine) vehicle.
Here are the key components of an EV;
- Electric Engine/Motor- Provides power to rotate the wheels. It can be DC/AC type.
- Inverter- Converts the electric current in the form of Direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC) for the vehicle’s motor if required.
- Drivetrain- EVs have a single-speed transmission which send power from the motor to the all the wheels.
- Batteries- Store the electricity required to run an EV. The higher the kW of the battery, the higher the driving range.
- Charging Port- plug into an outlet or EV charging point to charge your battery.
How are EVs charged ?

L1 vs L2 vs L3: Level of charging
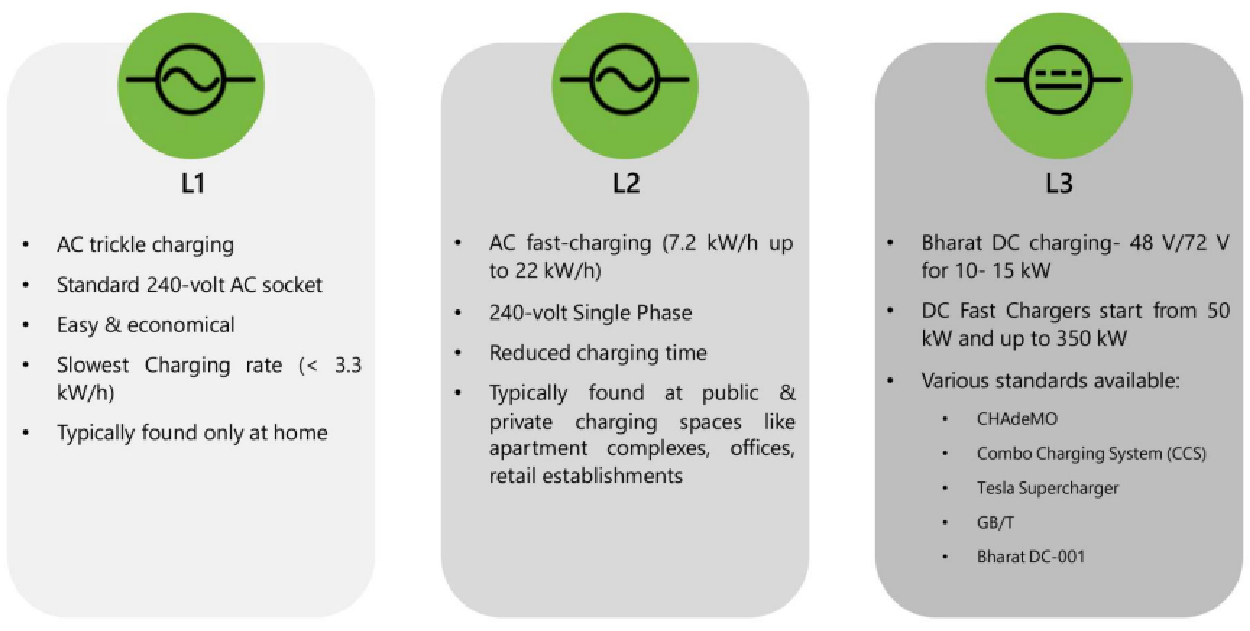
Where the AC Charging makes sense?

Where the DC charging makes sense?

DC chargers are mainly used for 4 wheelers that have very high utilization. These would includes scenarios, where
- You operate a commercial fleet and need fast charging to enhance your vehicle utilization.
- Heavy Vehicles –Cargos, Trucks which have large batteries and travels long distance-need access to fast charging.
- Highway fast chargers are required to support long distance Electrick vehicles.
- You are running a charge point network and need to install DC chargers as part of the Govt. mandate .
Where do people currently charge their Evs?

AC Charging vs DC Charging

AC Charger


Public AC Charger


DC Charger


DC Fast Charger 50KW





